Create a Winning Go To Market Strategy: Step-by-Step Guide
In our B2B Tech Guide to Go-To-Market Strategies, we outlined why a go-to-market strategy is central to the success of a product or business launch. Here we set out our tried and tested, seven-step approach to building a powerful strategy that will give your business the best chance of rapid growth and global success.
7-Step Framework to Nail Your Go To Market Strategy
1. Set SMART business goals and objectives
Begin by articulating your goals – what are you trying to achieve? – and your objectives – what do you need to do to achieve those goals?
When you do this, you should be guided by SMART principles: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Timebound.

Within these broader goals you should set quantitative objectives such as ‘generate £xxx within six months’ or ‘secure xxx new customers within four months of launch’ (measurable and timebound).
So your goal can’t be ‘business success’ but should be something specific like ‘build brand awareness in the fintech sector in France, Germany and The Netherlands’ or ‘establish product as mid-price competitor to xxxxxx’.
Ensuring your goals are attainable and relevant keeps your strategy realistic and avoids setting yourself up for failure by being overly ambitious.
2. Identify your target market and ideal customer
It’s important to realise that you can’t target every market and should focus on those that offer the greatest potential return. How do you identify them? First, list all potential target markets and then whittle down the list by assessing them against criteria such as: market size, growth trends, competitors, barriers to entry, culture, and cost of reaching the market. Your objective is to find a market where there is an evident gap that you can fill, or pain point that you can address – profitably.
Once you have identified your target market or markets you should turn your attention to getting to know your ideal customer persona within each. You need to know the demographics of your ideal customer, e.g. their age, gender, location, job role/title, education, interests, personality and buying habits. Develop a clear view of why these people would buy your product. Are you helping to solve a problem, or supporting them to achieve a specific goal? It pays to take the time to really get to know your customer. Top performing companies have mapped 90% or more of their customer database by persona.
3. Define your product-market fit
It’s vital that you ensure that your product is a fit for the market you are targeting. There really is little point trying to sell snow to the Inuit. A good product–market fit is vital for launch success. Essentially that means ensuring your product is solving a problem for a particular market segment and that customers will be willing to pay for your solution repeatedly. This idea of repeatable sales is key. But often businesses think they have achieved product–market fit when in fact they have failed to validate the need for their product. A recent analysis of over 100 startups who shut down last year found that 35% didn’t solve a valid customer problem.
To check that you’ve achieved product–market fit, you should analyse your business against these three criteria:
- Does your product solve the customers’ problem?
- Can you reach your customers cost-effectively?
Will your customers be happy to pay for the product (at a price that your business needs to be profitable)?
3 Elements of Product Market Fit

4. Consider your competitors and how you will position your business/product
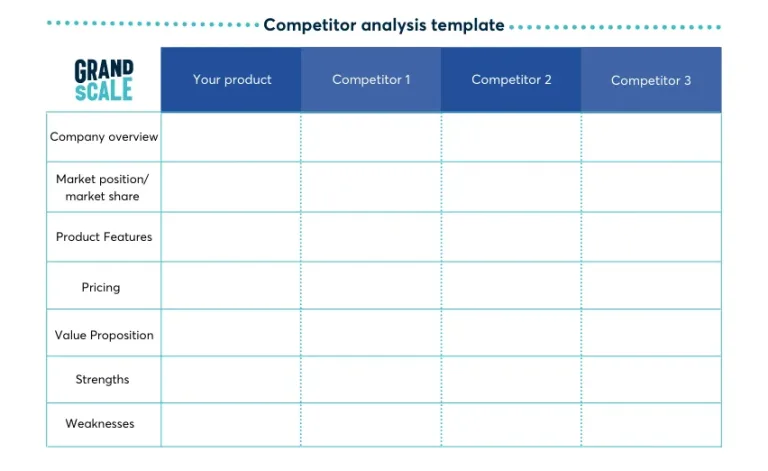
If you’ve come up with a product or service that is a world first, congratulations. More likely, there will be some level of competition in the market. Make sure you have an in-depth understanding of your competitors including market share, value proposition, pricing strategy, product features and user experience. How can you differentiate your offering to ensure you can secure the percentage of the market you need to meet your business growth targets?
A useful tool that will help you to understand your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses is a competitor analysis template (see example below). It allows you to consider where your competitors sit in relation to key attributes such as price and quality, and how your product compares. This information will help you refine your strategy.
Download your copy of our competitor analysis template.
5. Build a strong value proposition
A value proposition is a short clear statement that focuses on the outcome for the customer. This is an essential element of your go-to-market strategy. It explains what benefit you provide, for whom and how you do it uniquely well. This will be the centrepiece of your marketing and brand messaging. To help you crystallise your value proposition you can use Osterwalder’s ‘value proposition canvas’ shown here. It enables you to identify how your product(s) can help your potential customers ease their pain or support them to gain something they want.
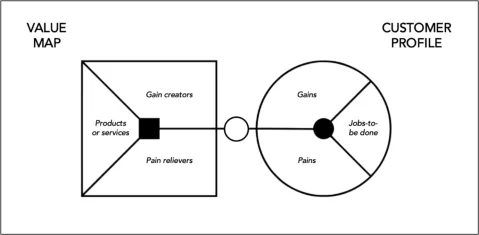
Source: Social Innovation Academy
6. Decide on your sales and pricing strategy
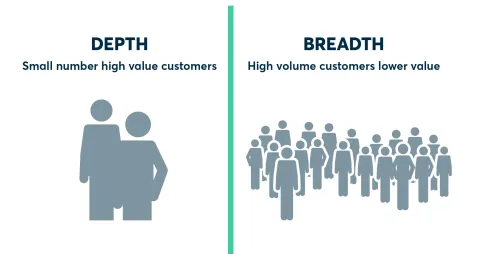
Your sales strategy must align with your SMART goals and objectives and be based on the target market you’ve identified. You need to consider what selling approach you will take. Will you use a volume play where you target a high number of prospects or take a niche approach where you nurture each account in-depth? Either way the focus must be on quality, qualified leads who will benefit from your product either by increasing their gain or decreasing their pain (see above).
Within your sales strategy you must decide on your pricing approach. How much does your product cost? Is that a realistic price point in your chosen market? What pricing options will you? Often new entrants to a market set a low price to gain some traction but be careful here as it can be difficult to increase your price afterwards and retain your market share.
There are lots of different pricing models to consider such as tiered pricing, which addresses the specific needs of different customers, loss-leading, bundles, per-feature, time-based and more, so take time to consider which approach best fits your product and market.
Sales Approach - Depth vs Breadth
7. Develop your marketing strategy
Now that you have a clear idea of the who, what, why, where and when of your go-to-market strategy, the next step is to consider the how – how you will reach and engage your target market and ideal personas and turn them into loyal customers. This is where your marketing strategy comes in. You need to develop a systematic process for building brand awareness with a high volume of ideal prospects and nurturing them through the sales funnel until they are ready to buy your product.
Building a go-to-market strategy is the essential first step in launching a new business or product. It pays to take the time to do it properly as it could be the difference between success and failure.
Go To Market Full Guide and Template
This proven 7-step framework will help you achieve a successful launch and give your business or product the best chance of securing market share.


